What Is The Endocannabinoid System (ECS)?

Christopher Visser
Multi-Cannabis Business Owner
Christopher Visser, the Founder and CEO of Cannabidiol Life and THCGummies.com, is a distinguished figure in the CBD industry, recognized for his pioneering contributions since 2016. With over 120 published articles, Christopher has become a reputable cannabis researcher, writer, and author. He's built two prosperous cannabis ventures that collectively generated millions in annual sales. His in-depth analysis of numerous cannabis studies, collaboration with medical professionals, and personal engagement with thousands of customers underline his expertise and commitment to advancing cannabis understanding daily.
-
 Written By:
Christopher Visser
Written By:
Christopher Visser
- Published:
- Updated: April 7, 2024
- 2 Comments: Feed The Flame?
Are you looking for a deeper understanding of your body? How about a 'secret' system that the majority of primary care physicians were never taught in medical school? If so, then it's time to introduce you to your complex and amazing Endocannabinoid System (ECS)!
Table of Contents
- Tags: ECS, Endogenous, Must Know
THE KEY POINTS:
THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM EXPLAINED IN UNDER 3 MINUTES & IN SIMPLE TERMS
The Endocannabinoid System is an intricate regulatory and signal management system within the human body. Not just humans, but also along with every other living organism that has a spine or that have cells with a nuclei.
As an FYI, the ‘ECS’ is the abbreviation for ‘Endocannabinoid System’, and is also called the Endogenous Cannabinoid System,
HOMEOSTASIS (total balance) is the primary role of the ECS and is critical in balancing neural, physical, and metabolic functions between the most notable body systems. The ECS adjusts the internal environment of the body to keep it running smoothly by fine-tuning the body’s functions, ensuring that various processes like pain sensation, inflammation, mood regulation, appetite, and memory are in balance.
1 MINUTE COMPLETE
How the ECS fine-tunes these functions is by modulating the internal communications between crucial biological systems and your brain to ensure that all of the mandatory everyday processes get taken care of without you having to lift a finger!
The ECS involves three main components:
- Endocannabinoids
- Cannabinoid Receptors
- Metabolic Enzymes
The ECS uses Endocannabinoids (“the keys”), which are chemical messengers, to interact with very specific site locations that are found on the cell walls in various tissues of our body, including your:
- brain
- organs
- connective tissues
- glands
- immune cells
These specific site locations are known as Cannabinoid Receptor Sites, which can be composed of 1 of 2 unique Cannabinoid Receptors; CB1 and CB2 Receptors (“the locks”).
Now, the ECS doesn’t directly send messages, nor does it communicate using electrical signals or ion channels like nerve cells do. Instead, its signaling process is purely chemical; using its endocannabinoids (chemical messengers) to bind to their respective cannabinoid receptors to relay messages.
2 MINUTES COMPLETE
Now, the ECS doesn’t directly send messages, nor does it communicate using electrical signals or ion channels like nerve cells do. Instead, its signaling process is purely chemical; using its endocannabinoids (chemical messengers) to bind to their respective cannabinoid receptors to relay messages.
The details of these messages involve instructions to restore balance regarding the number of signals (messages) being sent and received between systems of the body and the brain. Upregulating (increasing) or down regulating (decreasing) the number of signals is completely dependant on what the body needs at that particular moment.
The impacts of dysregulation of this system are NOTICEABLY experienced when you’re nervous system is overstimulated (anxious) and when your immune system response is faulty (pain caused by increased/prolonged inflammation).
IN SUMMARY:
The main role of ECS in our body is to achieve homeostasis, which is the body’s way of keeping its internal environment stable and functioning optimally. This involves a wide range of processes, from pain response and inflammation to sleep and immune function.
3 Minutes Complete!
You should now have a vivid understanding of the endocannabinoid system.
Now, we will continue with a much more in-depth article full of great research and information.
The 3 Key Components of the ecs
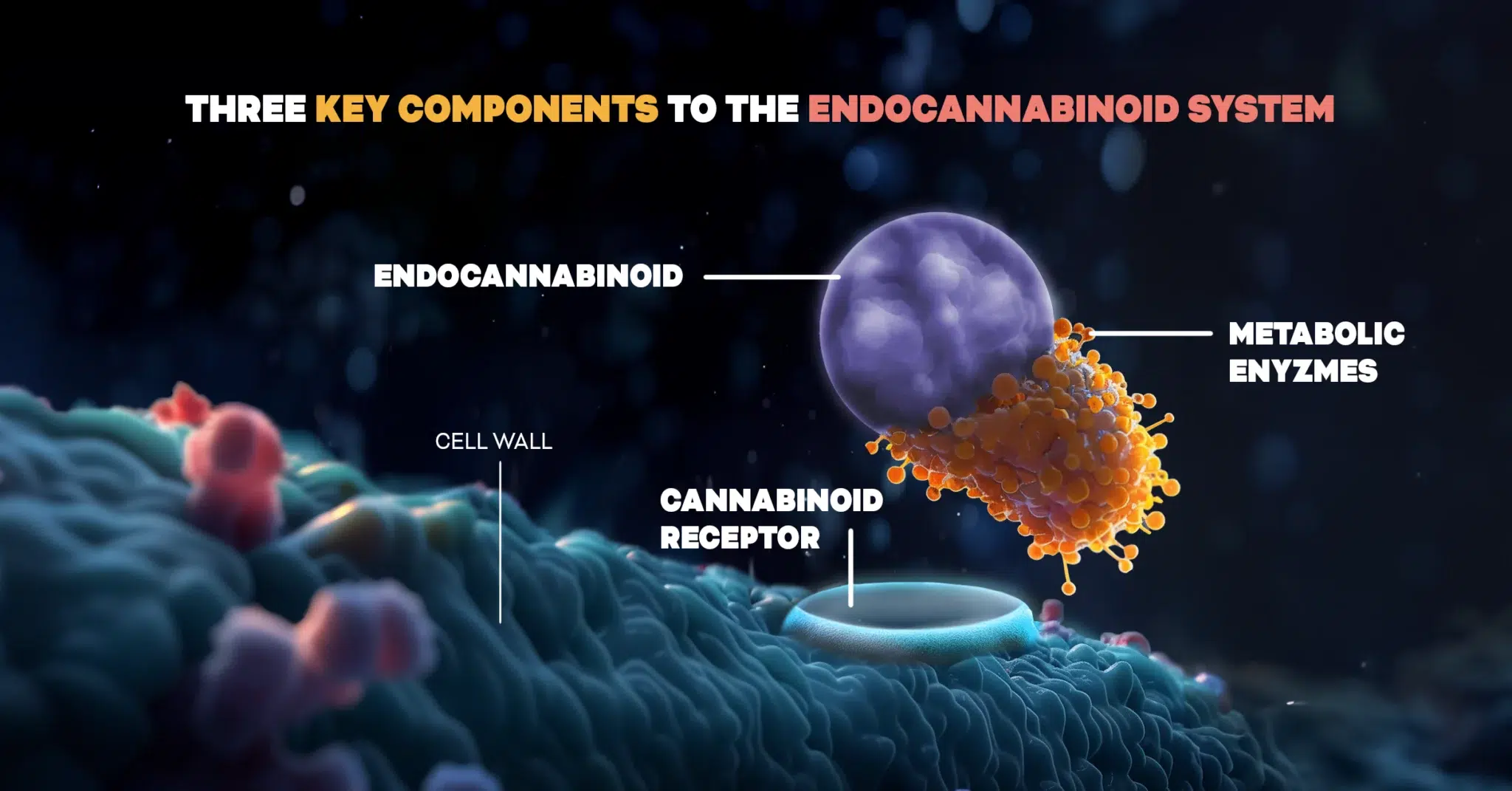
The three key parts within the ECS are the following:
- Endocannabinoids
- Cannabinoid receptors
- Metabolic enzymes
These three main components work together to ensure that the vital systems of the body work in a balanced and efficient way.
#1. Endocannabinoids: The Keys
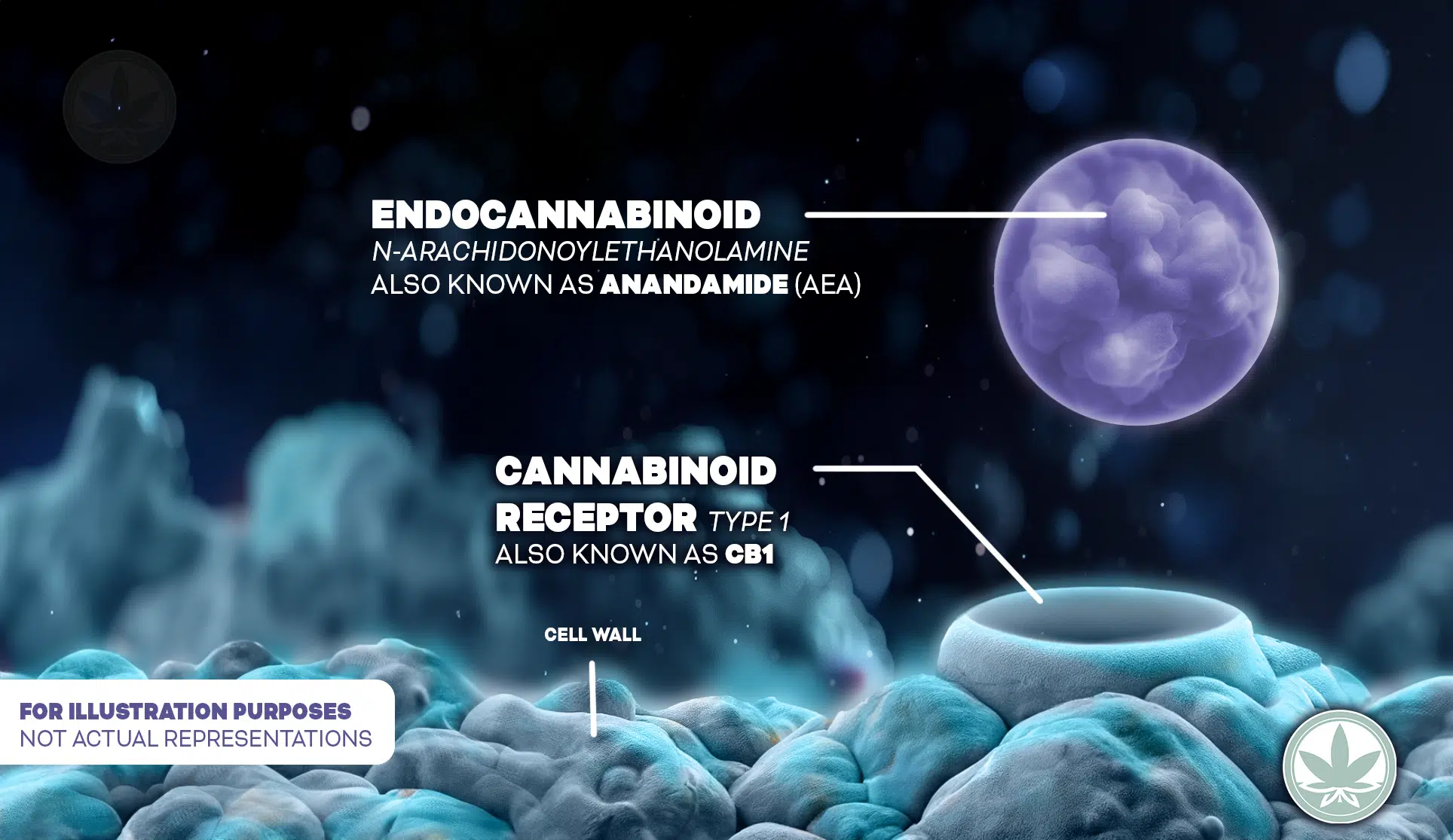
Endocannabinoids are cannabinoids that are produced within the human body.
FYI: Endo means “of/from within.”
These are endogenous neurotransmitters (a fancy word for endocannabinoid) which also defines it for being a native internal signaler of information (send and receive messages) bind to cannabinoid receptors (cannabinoid receptor proteins).
Two major endocannabinoids are anandamide and 2-AG. Anandamide plays a role in mood regulation and pain, while 2-AG is involved in appetite, immune system functions, and pain management.
Currently, science has identified 23 endocannabinoids and more are being identified as research evolves. Each endocannabinoid is involved in tuning many cognitive and physiological processes.
Endocannabinoids are the “keys” that fit into the “locks.“
#2. Cannabinoid Receptors (CBRs): The Locks
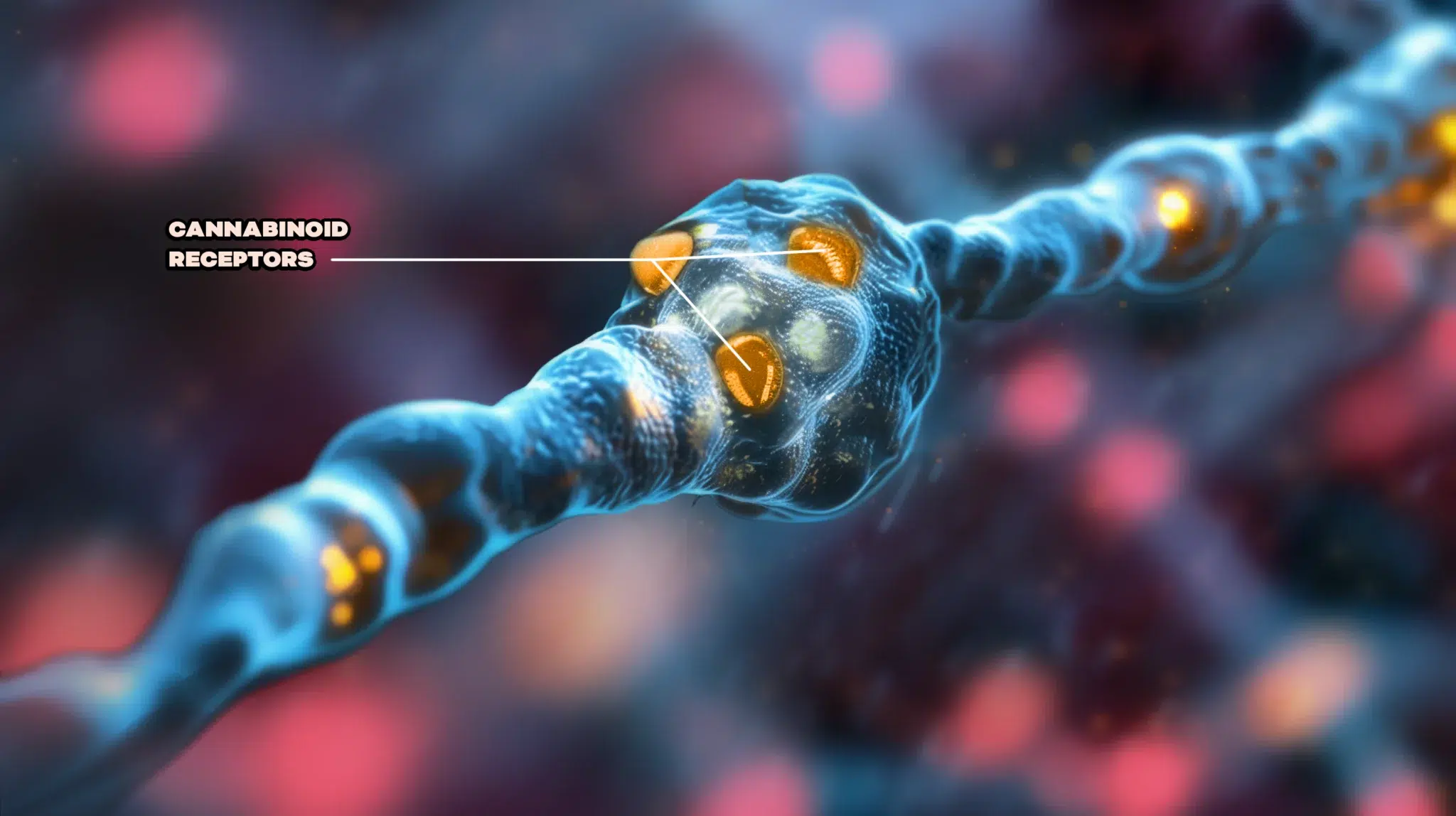
Cannabinoid receptors (CBRs) are receptor sites located on the cell walls of our cells and are found all-throughout the vertebrate, central, and peripheral nervous systems; think of them as locks.
The Keys (endocannabinoids) fit into these locks to send a message.
There are two primary Cannabinoid Receptors:
- CB1 Receptors – Found mainly in the brain, spinal cord, and nervous system. This particular CBR impacts and affects brain functions like mood and memory.
- CB2 Receptors – Found mostly in the immune system, influencing how we experience pain and inflammation.
#3. Metabolic Enzymes: The Catalytic Harmonizer

After the endocannabinoids that were produced to send a messege and the message gets sent to the brain (job completion), metabolic enzymes are produced by the body to “metabolize” them, AKA break them down.
This function restores balance and ensures that these messengers don’t continue sending messages and leaves room for new messengers to come in to send new messages to the brain if need be.
The main enzymes are FAAH, which breaks down anandamide, and MAGL, which breaks down 2-AG.
Vital BODY Systems The ECS Impacts
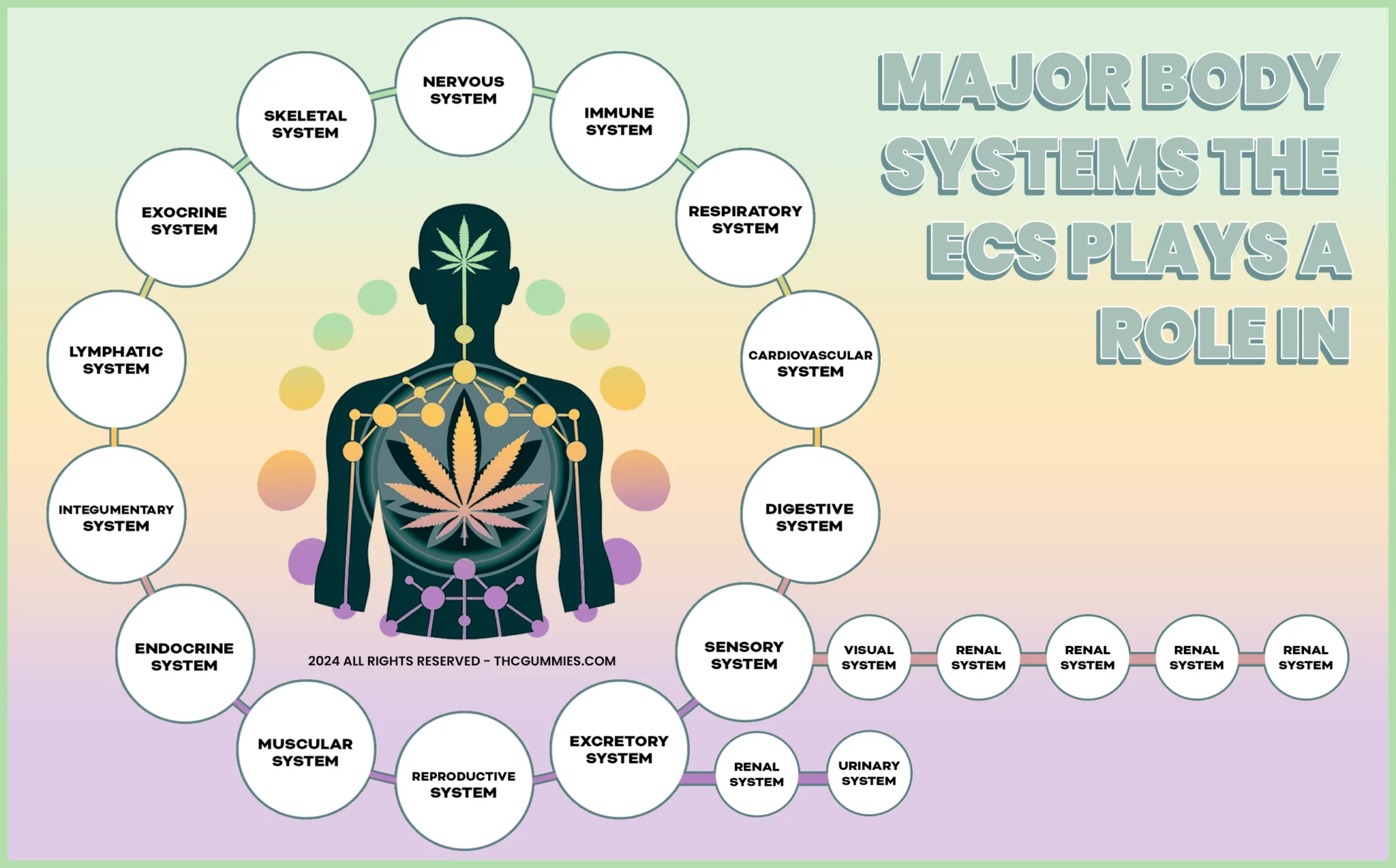
From the photo above, you can get a great look at all of the systems of the body that the ECS has a hand in regulating. To quickly cover how it’s involved, lets cover five of the vital body systems that the majority of readers are familiar with.
Further, by clicking on any of the dropdown boxes below, you’ll also see a list of health conditions associated with dysregulation/malfunctioning of that system.
1. Nervous System
With the nervous system, the ECS helps regulate the following:
- Mood and Emotional Regulation: ECS helps in managing conditions like anxiety, depression, and stress by influencing neurotransmitters.
- Pain Sensation: It modulates pain by interacting with pain signals in the brain. This is crucial for conditions like chronic pain, neuropathic pain, and post-operative pain.
- Memory and Learning: The ECS plays a role in memory formation and learning processes, impacting conditions like Alzheimer’s and other memory-related disorders.
- Appetite Control: It regulates hunger and satiety, affecting eating behaviors and disorders like obesity and anorexia.
- Sleep Regulation: The ECS helps in managing sleep patterns, impacting conditions like insomnia.
Function of ECS in Brain Communication:
When the ECS receives signals (through the interaction of endocannabinoids with their receptors), it can influence the brain’s response to various stimuli.
This includes regulating the release of neurotransmitters, which are the brain’s way of communicating with the body; sending electrical signals through neurons.
Now, have you ever felt suddenly overwhelmed?
It happens all of us.
Well, did you know that the neurons in our brains can have similar experiences?
Overwhelmed neurons is a great example that showcases the importance of cannabinoids in the human body.
OVER-EXCITED & OVER-STIMULATED
Endocannabinoids help alleviate the onslaught of signals, allowing the neurons to relax and recover. When a neuron gets overwhelmed, endocannabinoids communicate with it via its CB1 receptor, instructing it to dial back its signal transmission. This ensures receiving neurons aren’t overloaded with information.
It’s quite fascinating how endocannabinoids operate in a somewhat reverse fashion, sending what we call “retrograde” signals. These signals tell the body what to STOP doing instead of what to begin doing.
2. Immune System
ECS plays a role in managing the following:
- Inflammation Control: ECS regulates the body’s inflammatory responses, which is vital in conditions like arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
- Autoimmune Disorders: By modulating the immune response, the ECS is involved in the management of autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Pain Management: It also plays a role in reducing pain linked to inflammation.
Inflammation is our body’s defense mechanism.
When we sustain an injury or an infection, our immune system responds with inflammation to purge germs and damaged cells. However, there are times when this reaction can be excessive, spreading to regions where it’s unnecessary or persisting for longer than needed.
This typically occurs due to nerve damage or underlying health conditions, such as autoimmune diseases.
Endocannabinoids have demonstrated their ability to curb our immune system’s inflammatory response; and just like other immune cells, endocannabinoids are released in response to damage.
Similarly to how they operate in the brain to calm down over-stimulated neurons, this is another example of retrograde signaling, ensure that inflammation doesn’t get out of control.
If you didn’t know, excessive inflammation is the main cause for all health conditions.
3. Digestive System
The ECS has more receptors in the brain than any other receptor in the whole body. Do you know about your second brain? It’s your gut! And the ECS is involved with that too; influencing hunger signals and overall gut health.
Let’s organize this information neatly for clarity:
- Gut Motility: ECS influences the movement of the digestive tract, affecting conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Appetite Regulation: It plays a significant role in hunger signals, impacting eating disorders and weight management.
- Inflammation in the Gut: ECS helps in controlling inflammation in the gut, relevant in conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
4. Cardiovascular System
ECS can impact blood pressure and other heart-related functions. The ECS is the real deal, and anybody who tells you otherwise, is very ill-advised, ignorant, or evil.
I’ll refrain from opinions from now on. Here are the facts:
- Blood Pressure Regulation: ECS has a role in managing blood pressure, influencing conditions like hypertension.
- Arterial Health: It affects the health of arterial walls, relevant in atherosclerosis.
- Heart Rate Regulation: ECS influences heart rate and might impact conditions like arrhythmias.
5. Endocrine System
The ECS affects hormone production and regulation, impacting things like stress response and energy levels. Here are the specifics:
- Hormone Regulation: ECS modulates the secretion and action of various hormones, affecting stress response, metabolism, and sexual health.
- Energy Balance: It influences energy storage and expenditure, impacting conditions like diabetes and obesity.
- Stress Response: ECS plays a role in managing the body’s response to stress, affecting adrenal functions and stress-related disorders.
Each of these systems and the individual points within, highlight the intricate and extensive influence of the ECS on our health. It’s a system that:
- When balanced, it supports our well-being, leading to optimal body performance.
- When dysregulated, it can contribute to a variety of health issues and disorders.
CRITICAL THINKING:
Looking back at all your doctor visits, when was the last time your doctor told you to get your endocannabinoid levels checked?
PROOF THAT THE ECS EXISTS
I’m holding back my entire expert opinion for this section, that way there is no excuse that any offered reasoning can lead to the assumption of being biased.
The verifiable proof of the existence of the ECS are conveniently organized into the following three sections. Each section offers cited references for your verification.
Where The ECS Has Been Identified
What science has found are two very important points:
- All living creatures including
- If a cell has a nucleus, it
FOUND IN Literature For Medical Professionals
From the Medical Cannabis Handbook For Healthcare Professionals, in Chapter 3, it states the following:
Quotes By Medical Professionals, Doctors, Scientists, and Industry Professionals.
-
Dr. Ethan Russo
-
Dr. Tom Folan
-
ProjectCBD.org
Neglecting to educate medical professionals on the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is inexcusable, as it lies at the core of our physiology. Omitting this crucial information from healthcare curriculums strips away critical knowledge for treating patients and leaves a significant gap in trust between science and society.
Board-certified with the American Board of Radiology (ABR), member of the Association of Cannabis Specialists (ACS) and the American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM).
“It is absolutely criminal that we have physicians graduating medical schools like I did without learning a single thing about one of the largest systems in our body.”
ProjectCBD.org, one of the first educators in the cannabinoid and CBD space, calls the ECS the body’s master regulatory system.
RESEARCH STUDIES:
SPECIFIC HEALTH CONDITIONS & THE ECS
Click on the condition below that interests you to view at least four different studies with summaries of what researchers found regarding how the ECS impacts the health issue.
- Gruden et al. (2016) explored the role of the ECS in the development of type 2 diabetes and its complications. They found that the ECS is involved in the regulation of glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and inflammation, all of which are crucial factors in diabetes management.
- Horváth et al. (2012) investigated the potential of targeting the ECS for the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes. They concluded that modulating the ECS through the use of CB1 receptor antagonists or other compounds that influence endocannabinoid signaling could be a promising therapeutic approach for these conditions.
- Levendal et al. (2012) investigated the potential of cannabidiol (CBD) as a treatment for diabetes-related complications. They found that CBD could attenuate the development of diabetes-induced retinal neuroinflammation and cell death, suggesting that CBD may be a promising therapeutic agent for managing diabetic retinopathy.
- Weiss et al. (2006) explored the effects of the CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. They found that rimonabant improved glycemic control and reduced body weight, indicating that targeting the ECS could be a potential strategy for managing type 2 diabetes and obesity.
- Stanley et al. (2013) reviewed the role of the ECS in cardiovascular regulation and disease. They found that the ECS plays a critical role in modulating heart function, blood pressure, and vascular inflammation, suggesting that targeting the ECS could be a potential strategy for treating various cardiovascular disorders.
- Batkai et al. (2004) investigated the effects of endocannabinoids on blood pressure regulation in an animal model. They discovered that anandamide, an endocannabinoid, can lower blood pressure by activating CB1 receptors, indicating that the ECS is involved in the regulation of cardiovascular function.
- Pacher et al. (2008) reviewed the role of the ECS in cardiovascular disease and the potential therapeutic implications of targeting the ECS. They found that the ECS is involved in the regulation of various cardiovascular processes, such as vascular tone, inflammation, and cell survival, and that modulating the ECS could be a potential strategy for treating cardiovascular disorders.
- Steffens et al. (2005) investigated the effects of low-dose oral cannabinoids on atherosclerosis progression in an animal model. They found that treatment with a low dose of THC significantly reduced the progression of atherosclerotic lesions, suggesting that targeting the ECS could be a potential approach for managing atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular diseases.
- Ilyasov et al. (2018) explored the role of the ECS in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's. They found that the ECS is involved in the regulation of various processes that are disrupted in these disorders, such as neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and neuronal survival, suggesting that targeting the ECS could be a potential therapeutic strategy.
- Silvestri and Di Marzo (2013) reviewed the potential of ECS modulation for the treatment of epilepsy. They found that compounds targeting the ECS, such as CBD and other phytocannabinoids, showed promise in reducing seizure frequency and severity in various animal models and human studies, highlighting the therapeutic potential of the ECS in epilepsy management.
- Casajuana Kögel et al. (2020) reviewed the potential of the ECS as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. They found that modulating the ECS could help in reducing neuroinflammation, improving synaptic plasticity, and promoting neuronal survival, suggesting that targeting the ECS could be a promising strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
- Stampanoni Bassi et al. (2018) explored the role of the ECS in multiple sclerosis (MS) and the potential therapeutic implications of targeting the ECS in MS. They found that the ECS is involved in the regulation of neuroinflammation, demyelination, and neurodegeneration in MS, and that compounds targeting the ECS, such as cannabinoids, could be potential therapeutic agents for managing MS symptoms and progression.
- Barrie and Manolios (2017) investigated the role of the ECS in pain and inflammation. They found that the ECS is involved in the modulation of pain perception and the regulation of inflammatory processes, suggesting that targeting the ECS could be a potential strategy for managing chronic pain and inflammatory conditions
- Woodhams et al. (2017) reviewed the evidence for the use of cannabinoids in the treatment of pain. They concluded that compounds targeting the ECS, such as THC, CBD, and synthetic cannabinoids, showed promise in the management of various types of pain, including neuropathic, inflammatory, and cancer-related pain.
- Nagarkatti et al. (2009) investigated the role of the ECS in the regulation of immune responses and inflammation. They found that the ECS plays a critical role in modulating inflammatory processes and that targeting the ECS could be a potential strategy for treating various inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and multiple sclerosis.
- Russo (2008) reviewed the potential of cannabinoids for the treatment of difficult-to-treat pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia, migraine, and irritable bowel syndrome. He found that compounds targeting the ECS, particularly THC and CBD, showed promise in managing pain and associated symptoms in these conditions, highlighting the therapeutic potential of the ECS in the management of chronic pain disorders.
SUMMARY: IS THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM REAL?
INDISPUTABLE EVIDENCE:
In ORDER FOR A PERSON TO BE IN GOOD health, THE VITAL SYSTEMS OF THE BODY MUST function and communicate properly. Ensuring this is always accomplished is the main purpose of why the ECS exists within us; to manage the signals between the systems in order to maintain homeostasis (complete balance) within the body.
Are you thriving or surviving?
You can survive if the ECS starts malfunctioning by introducing medications. Albeit, it’ll be at the cost of disrupting other systems and causing secondary adverse effects from the additional disruption.
Further, medications are majoraly prescribed to help eliminate the symptoms without addressing the system that caused the symptom.
THIS IS WHY SUPPORTING THE ECS IS SO IMPORTANT.
For your body to thrive and work optimally, the ECS must be a priority.
THE DISCOVERY OF THE ECS: With A FULL TIMELINE OF HISTORIC Findings

| DATE | DESCRIPTION | RESEARCHERS INVOLVED | SOURCE |
|---|---|---|---|
| December 1932 | The structure of CBN was elucidated. | Robert Sidney Cahn | https://doi.org/10.1002/jlac.19324970111 |
| January 1940 | Chemical synthesis of CBN was achieved in the U.S.A. and U.K. | Roger Adams (U.S.A.), Alexander Robertus Todd (U.K.) | https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01858a058 |
| January 1940 | Cannabidiol (CBD) was first obtained from cannabis. | Roger Adams, Madison Hunt, J. H. Clark | https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01858a058 |
| October 1942 | THC was first extracted from cannabis. | H. J. Wollner, J. R. Matchett, S. Loewe | https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01263a054 |
| April 1964 | THC was isolated, synthesized, and identified as the main psychoactive compound in cannabis. | Raphael Mechoulam, Yehiel Gaoni, Haviv Edery, M. Grunfeld | https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01062a046 |
| August 1988 | The first cannabinoid receptor, CB1, was discovered in the brain of a rat. | Allyn Howlett, William Devane | https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-3908(88)90208-5 |
| August 9, 1990 | The DNA sequence that defines the THC-sensitive receptor in the rat brain was pinpointed. | Lisa Matsuda, Allyn Howlett | https://doi.org/10.1038/346561a0 |
| December 18, 1992 | The first endogenous cannabinoid, anandamide (AEA), was discovered. | William Devane, Lumir Hanus, Lumír Ondřej Hanuš, Raphael Mechoulam | https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1470919 |
| September 2, 1993 | The second cannabinoid receptor, CB2, was cloned. | Sean Munro, Kerrie L. Thomas, Muna Abu-Shaar | https://doi.org/10.1038/365061a0 |
| June 1995 | 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) was identified. | Raphael Mechoulam, Shimon Ben-Shabat, Lumír Ondřej Hanuš (Israel), Takayuki Sugiura, Seishi Kishimoto, Keizo Waku (Japan) | https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(95)00109-D |
| December 20, 1996 | The metabolic enzyme responsible for the breakdown of anandamide, FAAH, was identified. | Benjamin F. Cravatt, Dale L. Boger | https://doi.org/10.1126/science.274.5295.2081 |
| November 27, 1998 | The concept of the “entourage effect” was introduced. | Shimon Ben-Shabat, Raphael Mechoulam | https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(98)01175-5 |
| October 4, 2002 | The metabolic enzyme responsible for the breakdown of 2-AG, MAGL, was identified. | Tiziana Bisogno, Natalia Battista, Monica Bari, Dominique Piomelli | https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m202878200 |
| July 1, 2004 | The idea of Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency (CED) was proposed. | Ethan Russo | https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2004.10400015 |
| August 2, 2012 | The presence of CB1 receptors on mitochondrial membranes was discovered. | Giovanni Marsicano, Michaël Lafenêtre, Fabricio A. Moreira | https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11127 |
Four Types of Cannabinoids That Interact WIth The ECS
There are four types of cannabinoids:
- Endocannabinoids – These are our biological endogenous cannabinoids that are naturally created by the human body.
- Phytocannabinoids – These cannabinoids are also 100% natural, but they are created by plants, especially cannabis plants (marijuana and hemp).
- Synthetic Cannabinoids – These cannabinoids are NOT naturally derived and are created by taking compounds from non-cannabis plants and chemically altering them to have similar molecular structure like those found in endocannabinoids.
- Semi-Synthetic Cannabinoids – These cannabinoids began as natural phytocannabinoids from cannabis plants, but have been chemically altered to produce another natural phytocannabinoid because the originating phytocannabinoid is not produced in substantial quantities on its own for use at a commercial scale.
Where Cannabis Comes In: Intro to Phytocannabinoids & How CBD, THC, & Others Offer Value
Phytocannabinoids are cannabinoids that are very similar to the endocannabinoids produced by the body, but are naturally produced within plants, cannabis flowers specifically.
Phyto means “of/from a plant.”
Currently, 151 phytocannabinoid and cannabinoid derivatives have been identified, with each seemingly to offer unique effects and specific therapeutic value.
The easiest way of conceptualizing why phytocannabinoids have therapeutic value is because their molecular structures are incredibly similar to the molecular structures of the Endocannabinoids that our bodies produce.
So, phytocannabinoids, like endocannabinoids, have an affinity for (are attracted to) the cannabinoid receptors within the ECS, mimicking the same call signal that the endocannabinoid would produce if it connected to a cannabinoid receptor.
Understanding the similarities and differences between Endocannabinoids and Phytocannabinoids is essential for understanding their medicinal effects on the endocannabinoid system.
How CBD & THC INTERACT WITH THE ECS
TETRAHYDROCANNABINOL (THC)
THC attaches itself to two components in our bodies: CB1 and CB2 receptors. But it has a particular affinity for CB1, which is primarily responsible for the effects of THC.
These effects can range from dependence and pain to mood alterations and appetite changes.
CANNABIDIOL (CBD)
Then we have CBD, another compound found in cannabis. It’s not particularly fond of the CB1 receptor, but it certainly interacts well with various other receptors in our brains.
TETRAHYDROCANNABIVARIN (THCV)
Also known as Virodhamine, when THCV is ingested in low doses, THCV inhibits appetite, regulates blood sugar levels, and reduces the body’s resistance to insulin.
To learn more: Visit our What is THCV article.
For Products: View our THCV gummies collection.
Phytocannabinoid Therapeutic Value With Real-Life Examples
- Suppose you have a deficiency of the endocannabinoid called 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). In that case, you may be able to supplement the lack of 2-AG by ingesting its phytocannabinoid equivalent, cannabidiol (CBD), as both interact with the body’s CBRs in the same way.
- Suppose you have a deficiency of the endocannabinoid called anandamide (AEA). In that case, you may be able to alleviate by supplementing with AEAs phytocannabinoid equivalent, Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
The theory of phytocannabinoid supplementation for treating endocannabinoid deficiency disorders explains the “how” and the “why” botanic cannabinoid medicines may have incredible therapeutic value.
Crucial Functions That Maintain Our Well-being
Now, let’s delve into two specific functions our bodies perform that are crucial for maintaining homeostasis: managing the nervous system and controlling inflammation. They’re incredibly important because if either of these goes awry, it can potentially lead to various health issues.
Endocannabinoid Deficiency (CECD)
As we age, natural and harmful environmental factors impact our bodies. These expected and unexpected impacts can make a person deficient in particular Endocannabinoids; hence “Endocannabinoid Deficiency.”
A body becomes deficient, can also cause certain functions within the Immune, Digestive, or Central nervous system can become compromised.
As this occurs, science now acknowledges the possibility of supplementing the deficiency or broken function by introducing the body via inhalation or ingestion of the equivalent or similar chemical compound (like CBD or THC) to help up-regulate or down-regulate the overexcited or under-excited Endocannabinoids in order to help balance out the deficiencies; thriving effortlessly to support homeostasis throughout your body.
Video Playlist: Ted Talks, Podcasts, & Interviews About The ECS
Take a deep dive into your endocannabinoid system.
Final Thoughts
Research into the Endocannabinoid System is still impacted by federal laws which hinder researchers ability to conduct research at will. Clearly, this makes it difficult for scientists to pursue truth in this area.
By opening the doors to more cannabis and marijuana research without constraint, science can make longer strides to better understand the connection between ECS dysregulation and endocannabinoid deficiencies with specific medical conditions and health disorders that are occur as we age.
The moment researchers can accomplish this, the medicine society would have the ability to start addressing the system rather than masking the symptom.
BUT, DO YOU THINK THAT IS WHAT BIG PHARMA WANTS TO ACCOMPLISH?
Please leave your comments, thoughts, and answers below!
References
Woodhams, S. G., Sagar, D. R., Burston, J. J., & Chapman, V. (2015). The Role of the Endocannabinoid System in Pain. Pain Control, 119–143. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-662-46450-2_7
Cluny, N. L., Keenan, C. M., Reimer, R. A., Le Foll, B., & Sharkey, K. A. (2015). Prevention of Diet-Induced Obesity Effects on Body Weight and Gut Microbiota in Mice Treated Chronically with Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol. PLOS ONE, 10(12), e0144270. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144270
Lu, H. C., & Mackie, K. (2016). An Introduction to the Endogenous Cannabinoid System. Biological Psychiatry, 79(7), 516–525. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.07.028
Di Marzo, V., & Piscitelli, F. (2015). The Endocannabinoid System and its Modulation by Phytocannabinoids. Neurotherapeutics, 12(4), 692–698. DOI: 10.1007/s13311-015-0374-6
Carnevale, L. N., Arango, A. S., Arnold, W. R., Tajkhorshid, E., & Das, A. (2018). Endocannabinoid virodhamine is an endogenous inhibitor of human cardiovascular CYP2J2 epoxygenase. Biochemistry, 57(46), 6489-6499. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00691
Dawson, D.A. (2018). Synthetic cannabinoids, organic cannabinoids, the endocannabinoid system, and their relationship to obesity, diabetes, and depression_. Mol Biol 7_: 219. https://doi.org/10.4172/2168-9547.1000219
Katchan, V., David, P., & Shoenfeld, Y. (2016). Cannabinoids and autoimmune diseases: A systematic review. Autoimmunity Reviews, 15(6), 513-528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2016.02.008
Russo, E. B. (2008). Cannabinoids in the management of difficult to treat pain. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, 4(1), 245–259. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2503660/
DiPatrizio, N. V. (2016). Endocannabinoids in the Gut. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, 1(1), 67–77. DOI: 10.1089/can.2016.0001
Pacher, P., Bátkai, S., & Kunos, G. (2006). The Endocannabinoid System as an Emerging Target of Pharmacotherapy. Pharmacological Reviews, 58(3), 389–462. DOI: 10.1124/pr.58.3.2

If this article sparked a new insight, pass the flame…
LET’S IGNITE RIPPLES OF CANNABIS WISDOM.
Be the catalyst for someone’s breakthrough moment.
SHARE ON SOCIAL MEDIA

YOUR CANNABIS EDIBLE
JOURNEY CONTINUES:
Looking For Something Else?









2 Responses
Thanks for reaching out! Which point of view would you like us to expand on? Thanks, 20Bet!
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.